COM20022I Ver la hoja de datos (PDF) - SMSC -> Microchip
Número de pieza
componentes Descripción
Lista de partido
COM20022I Datasheet PDF : 88 Pages
| |||
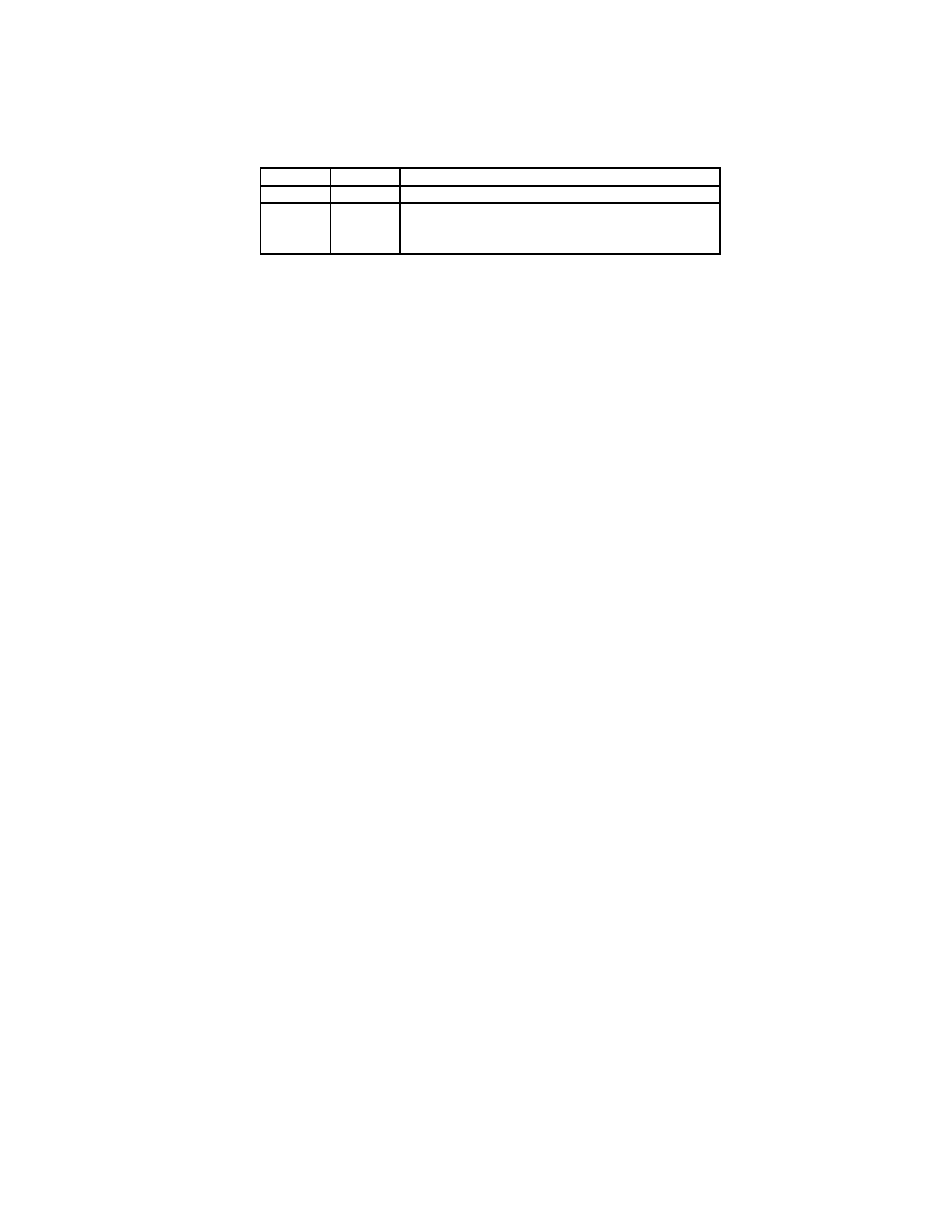
Selecting Clock Frequencies Above 2.5 Mbps
To realize a 10 Mbps network, an external 80
MHz clock must be input. However, since 80
MHz is the frequency of FM radio band, it is not
practical for use for noise emission reasons.
Therefore, higher frequency clocks are
generated from the 20 MHz crystal as selected
through two bits in the Setup2 register,
CKUP[1,0] as shown below. The selected clock
is supplied to the ARCNET controller.
CKUP1
0
0
1
1
CKUP0
0
1
0
1
CLOCK FREQUENCY (DATA RATE)
20 MHz (Up to 2.5Mbps) Default (Bypass)
40 MHz (Up to 5Mbps)
Reserved
80 MHz (Only 10Mbps)
This clock multiplier is powered-down
(bypassed) on default. After changing the
CKUP1 and CKUP0 bits, the ARCNET core
interfere
with the next INVITATION TO
TRANSMIT, destroy the token and keep any other
node from assuming control of the line.
operation is stopped and the internal PLL in the
clock generator is awakened and it starts to
generate the 40 MHz or 80 MHz. The lock out
time of the internal PLL is 8uSec typically. After
more than 8 #sec (this wait time is defined as 1
msec in this data sheet), it is necessary to write
command data '18H' to the command register to
re-start the ARCNET core operation. This clock
generator is called “clock multiplier”.
Changing the CKUP1 and CKUP0 bits must be
one time or less after releasing a hardware
reset.
When any COM20022 senses an idle line for
greater than 20.5 S, which occurs only when the
token Is lost, each COM20022 starts an internal
timeout equal to 36.5 s times the quantity 255
minus its own ID. The COM20022 starts network
reconfiguration by sending an invitation to transmit
first to itself and then to all other nodes by
decrementing the destination Node ID. If the
timeout expires with no line activity, the
COM20022 starts sending INVITATION TO
TRANSMIT with the Destination ID (DID) equal to
the currently stored NID. Within a given network,
only one COM20022 will timeout (the one with the
The EF bit in the SETUP2 register must be set
when the data rate is over 5 Mbps.
highest ID number). After sending the
INVITATION TO TRANSMIT, the COM20022
waits for activity on the line. If there is no activity
NETWORK RECONFIGURATION
A significant advantage of the COM20022 is its
ability to adapt to changes on the network.
Whenever a new node is activated or deactivated,
a NETWORK RECONFIGURATION is performed.
When a new COM20022 is turned on (creating
a new active node on the network), or if the
for 18.7 S, the COM20022 increments the NID
value and transmits another INVITATION TO
TRANSMIT using the NID equal to the DID. If
activity appears before the 18.7 S timeout
expires, the COM20022 releases control of the
line. During NETWORK RECONFIGURATION,
INVITATIONS TO TRANSMIT are sent to all NIDs
(1-255).
COM20022 has not received an INVITATION TO
TRANSMIT for 210mS, or if a software reset
occurs, the COM20022 causes a NETWORK
RECONFIGURATION by sending a
RECONFIGURE BURST consisting of eight
marks and one space repeated 765 times. The
purpose of this burst is to terminate all activity
on the network. Since this burst is longer than
any other type of transmission, the burst will
Each COM20022 on the network will finally have
saved a NID value equal to the ID of the
COM20022 that it released control to. At this
point, control is passed directly from one node to
the next with no wasted INVITATIONS TO
TRANSMIT being sent to ID's not on the network,
until the next NETWORK RECONFIGURATION
occurs. When a node is powered off, the previous
node attempts to pass the token to it by issuing an
10