RT9167 Ver la hoja de datos (PDF) - Richtek Technology
Número de pieza
componentes Descripción
Lista de partido
RT9167 Datasheet PDF : 13 Pages
| |||
RT9167/A
Load-Transient Considerations
The RT9167/A load-transient response graphs (see Typical
Operating Characteristics) show two components of the
output response: a DC shift from the output impedance
due to the load current change, and the transient response.
The DC shift is quite small due to the excellent load
regulation of the IC. Typical output voltage transient spike
for a step change in the load current from 0mA to 50mA is
tens mV, depending on the ESR of the output capacitor.
Increasing the output capacitor's value and decreasing the
ESR attenuates the overshoot.
Shutdown Input Operation
The RT9167/A is shutdown by pulling the EN input low,
and turned on by driving the input high. If this feature is
not to be used, the EN input should be tied to VIN to keep
the regulator on at all times (the EN input must not be left
floating).
To ensure proper operation, the signal source used to
drive the EN input must be able to swing above and below
the specified turn-on/turn-off voltage thresholds which
guarantee an ON or OFF state (see Electrical
Characteristics). The ON/OFF signal may come from
either CMOS output, or an open-collector output with pull-
up resistor to the RT9167/A input voltage or another logic
supply. The high-level voltage may exceed the
RT9167/A input voltage, but must remain within the
absolute maximum ratings for the EN pin.
Internal P-Channel Pass Transistor
The RT9167/A features a typical 1.1Ω P-Channel MOSFET
pass transistor. It provides several advantages over similar
designs using PNP pass transistors, including longer
battery life. The P-channel MOSFET requires no base
drive, which reduces quiescent current considerably. PNP-
based regulators waste considerable current in dropout
when the pass transistor saturates. They also use high
base-drive currents under large loads. The RT9167/A does
not suffer from these problems and consume only 80μA of
quiescent current whether in dropout, light-load, or heavy-
load applications.
Input-Output (Dropout) Voltage
A regulator's minimum input-output voltage differential
(or dropout voltage) determines the lowest usable supply
voltage. In battery-powered systems, this will determine
the useful end-of-life battery voltage. Because the RT9167/
A uses a P-Channel MOSFET pass transistor, the dropout
voltage is a function of drain-to-source on-resistance
[RDS(ON)] multiplied by the load current.
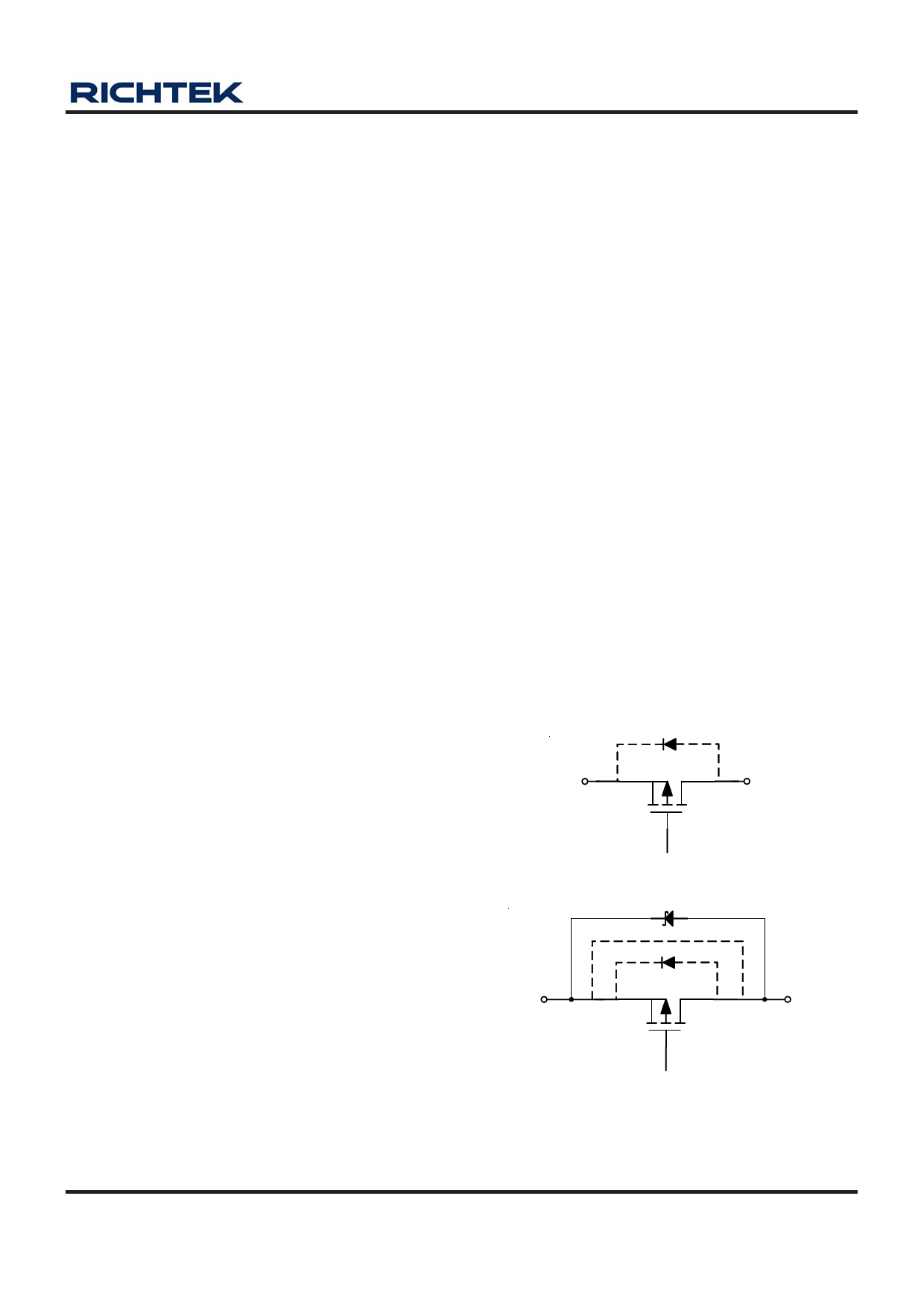
Reverse Current Path
The power transistor used in the RT9167/A has an inherent
diode connected between the regulator input and output
(see Figure 3). If the output is forced above the input by
more than a diode-drop, this diode will become forward
biased and current will flow from the VOUT terminal to VIN.
This diode will also be turned on by abruptly stepping the
input voltage to a value below the output voltage. To prevent
regulator mis-operation, a Schottky diode should be used
in any applications where input/output voltage conditions
can cause the internal diode to be turned on (see Figure4).
As shown, the Schottky diode is connected in parallel
with the internal parasitic diode and prevents it from being
turned on by limiting the voltage drop across it to about
0.3V. < 100mA to prevent damage to the part.
VIN
VOUT
Figure 3
VIN
VOUT
Figure 4
DS9167/A-26 March 2007
www.richtek.com
9