L7046 Ver la hoja de datos (PDF) - Hamamatsu Photonics
Número de pieza
componentes Descripción
Lista de partido
L7046 Datasheet PDF : 14 Pages
| |||
1) Main Power Supply
Besides supplying the lamp with stable dc power, the main
power supply keeps the cathode at the optimal operating
temperature with a specified current. The cathode tempera-
ture is very important for lamps: when too high, evaporation
of the cathode materials is accelerated; when too low, work
function becomes worse, causing cathode sputtering which
greatly reduces the lamp’s life.
The lamp current must be set within a specified range to
ensure lamps to operate stably for a long time. For this rea-
son, each wattage lamp has their respective operating lamp
current values and ranges. Since the radiant intensity is ap-
proximately in proportion to the lamp current values (as
agreed from Figure 9), the power supply must be designed
with higher stability than is required from the lamp.
2) Trigger Power Supply
This is for starting the lamp to discharge. As shown in Fig-
ure 4, it gives a high frequency triggering pulse to the lamp
load by inductive coupling. The lamp’s initial discharge char-
acteristic is that its starting voltage is approximately 10 kV.
However, the characteristic fluctuates according to cathode
fatigue or variations of the filled-in gas pressures. There-
fore, in actual devices a triggering voltage of approximately
20 to 25 kV should be applied, taking safety margin into
consideration as well.
CHARACTERISTICS
With regard to data which differs with the wattage ratings, a
typical example would be the use of a 200 W lamp (type
L2423). The unspecified data that is given, applies to all the
lamps irrespective of the wattage of lamp.
1) Spectral Distribution
The radiation spectrum of the lamp has strong brilliant line
spectra from the ultraviolet to the visible range. Figure 5
shows the radiated spectral distribution, for Mercury-Xenon
lamps and other lamps. This spectral distribution includes
both the radiation spectrum of a Xenon lamp and brilliant
mercury line spectra.
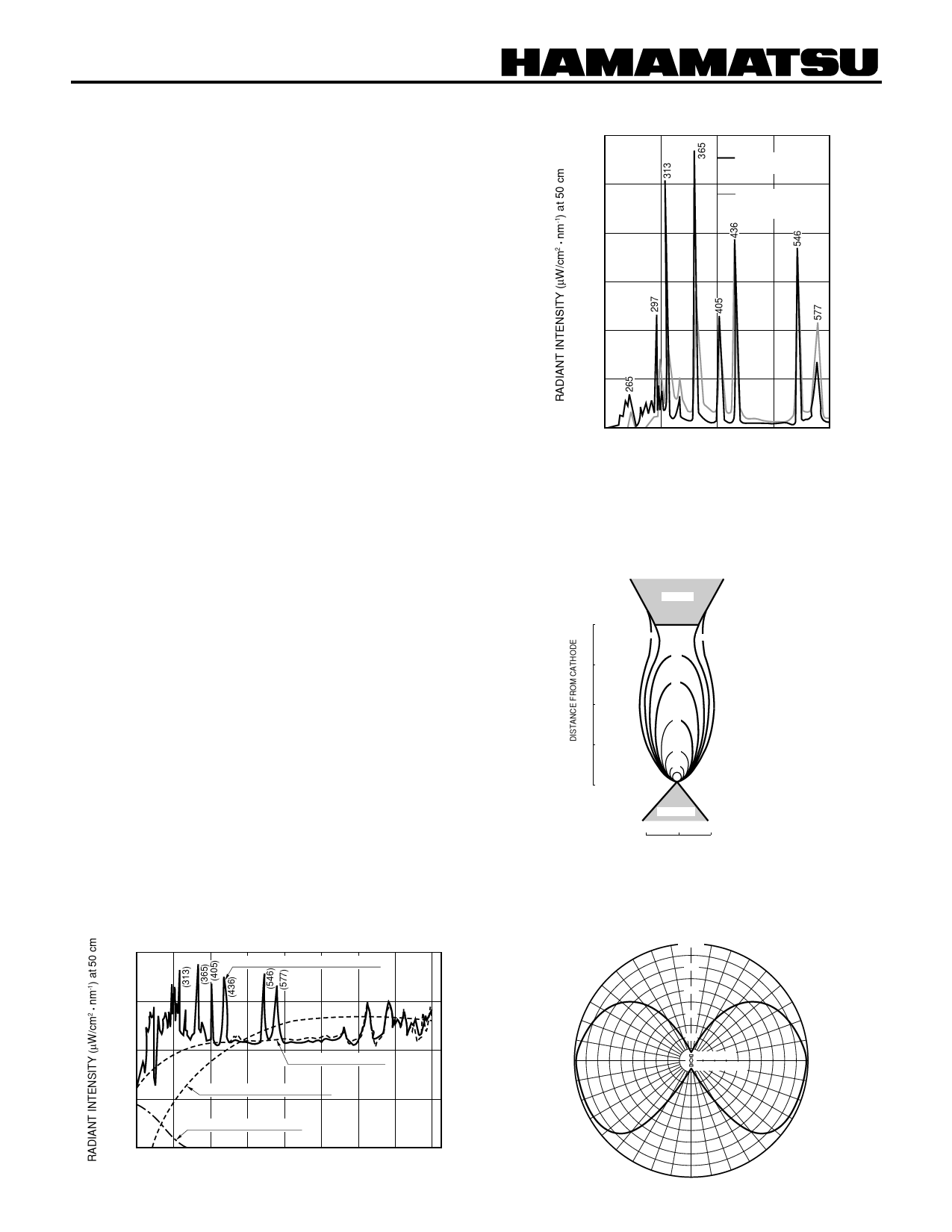
Figure 6 shows a comparison of the radiated spectral distri-
bution of a Mercury-Xenon Lamp and a super-high-pres-
sure mercury lamp. Compared to the super-high-pressure
mercury lamp, the Mercury-Xenon Lamp provides greater
radiation intensity in the deep UV range from 300 nm down-
ward, and is characterized by sharp line spectra with high
peak.
Figure 5: Spectral Distribution of Various Lamps
TLSXB0085EC
100
MERCURY-XENON LAMP (200 W)
10
1
XENON LAMP (150 W)
HALOGEN LAMP (24 V -150 W)
0.1
DEUTERIUM LAMP (30 W)
0.01
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
WAVELENGTH (nm)
3
Figure 6: Comparison of Mercury-Xenon Lamp with
Super-High-Pressure Mercury Lamp
60
MERCURY-XENON
LAMP (200 W)
50
SUPER-HIGH-
PRESSURE MERCURY
LAMP (200 W)
40
30
20
10
0
200
300
400
500
600
WAVELENGTH (nm)
TLSXB0078EA
2) Luminance Distribution
Maximum luminance is located nearby the cathode, and it
decreases towards the anode. Figure 7 shows the luminance
for a 200 W lamp distribution relative to the cathode area.
Figure 7: Luminance Distribution (200 W Lamp L2423)
(mm)
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
ANODE
30 40(%) 30
50
60
LAMP CURRENT 8.0 A dc
AMBIENT TEMP. 25 °C
70
80
90
100
CATHODE
0.5
0
0.5
ARC WIDTH (mm)
TLSXC0032EA
3) Flux Distribution
Figure 8 shows the flux distribution of the lamps. It has
uniform distribution in the horizontal direction.
Figure 8: Flux Distribution (at Vertical Operation)
200°
180°
100 %
160°
220°
80
140°
60
240°
40
120°
260°
280°
20
+ ANODE
- CATHODE
100°
80°
300°
60°
320°
40°
340°
20°
0°
TLSXC0031EA